Frequently Asked Questions
Incoterms & Trade Terms
What are Incoterms?
International commercial terms that define who bears costs, risks, and responsibilities at each stage of a shipment.
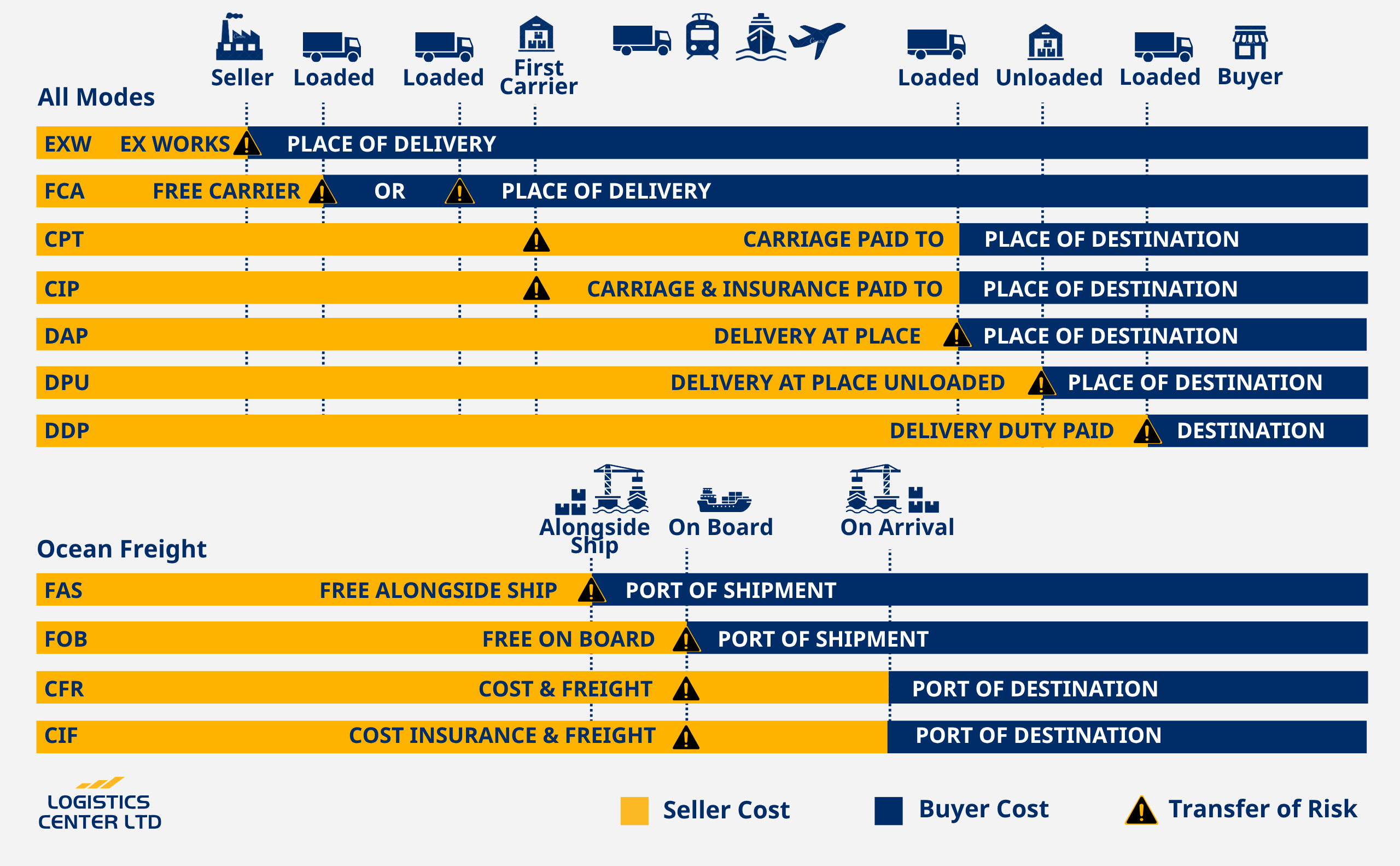
What are the most common Incoterms?
- EXW (Ex Works): Buyer collects at the seller’s premises and assumes all further obligations.
- FCA (Free Carrier): Seller delivers to the carrier chosen by the buyer.
- FOB (Free On Board): Seller is responsible until the goods are loaded on the vessel.
- CFR (Cost & Freight): Seller pays freight to the destination port; risk transfers upon loading.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance & Freight): As per CFR, plus seller provides insurance.
- DAP (Delivered At Place): Seller delivers to the agreed point in the destination country.
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid): Seller covers everything, including duties/taxes, to the buyer’s door.
Free Zone
What is a Free Zone?
A special area within a port, airport or border where imported goods are subject to a suspension of duties and taxes. Its main purpose is to facilitate international trade and increase transit trade by offering favorable customs conditions. Within the zone, goods may be stored, repackaged or processed, with duties and taxes being paid only when they are released into free circulation in the country.
What are the advantages of a Free Zone?
- Duty and VAT Suspension: Goods may be imported without the immediate payment of import duties, VAT and excise duties. Payment may be deferred until the final destination of the goods is determined.
- Improved cash flow management: The suspension of the VAT payment obligation improves the liquidity management of the business.
- Reliefs on goods: Goods destined for other EU member states are exempt from VAT.
Transport & Logistics
What does 3PL mean?
3PL (Third-Party Logistics) is the assignment of supply chain operations, such as warehousing, inventory management, to an external, third-party company and product shipping. This allows businesses to focus on their core business, while the 3PL provider takes over the distribution and shipping functions to end customers.
What is Freight Forwarding?
It is the organization and management of the transport of goods, usually internationally, on behalf of others. A freight forwarder is the intermediary who coordinates transportation by air, sea, rail or road, taking on the paperwork, customs procedures, warehousing and negotiating with carriers to ensure a safe and economical shipment.
What do FTL and LTL mean?
- FTL (Full Truck Load): One truck filled exclusively with one shipper’s cargo.
- LTL (Less than Truck Load): One truck shared by multiple shippers’ smaller consignments.
What do FCL and LCL mean?
- FCL (Full Container Load): One container filled exclusively with one shipper’s cargo.
- LCL (Less than Container Load): One container shared by multiple shippers’ smaller consignments.
What is demurrage?
Fee imposed for exceeding the agreed “free time” of a cargo in a port or terminal. Essentially, these are payments that charge for delays in loading, unloading or receiving a container after the end of the free period. These fees are usually calculated per day and are intended to compensate owners for the use of their equipment and premises.
What is IMO cargo?
Dangerous cargo transported by sea, according to the regulations of the International Maritime Organization (IMO). These cargoes are classified into 9 hazard categories, such as explosives, gases, flammable liquids, toxic, radioactive and corrosive materials.
What is ADR?
The international agreement governing the transport of dangerous goods (e.g., chemicals, flammables).
What is Drayage transportation?
It is the transport of goods over short distances, usually within an urban area, which acts as a critical link in the supply chain. It usually involves the movement of containers to or from ports, railway stations or warehouses, connecting various modes of transport, such as ships, trains and trucks.
What is cross-docking?
Goods are received and dispatched immediately without interim storage.
Customs Procedures
What is an EORI number?
The EORI number is a unique number used by EU customs authorities to identify business operators engaged in commercial activities governed by customs legislation. It acts as a “Tax Identification Number” for customs transactions within the Union and is necessary for imports, exports and other customs procedures.
What is customs warehousing?
Storage in a customs warehouse with suspension of duties and taxes until final disposition.
What is transit (T1, T2)?
- T1: For non-Union goods moving within the EU without paying duties/taxes until the final customs office.
- T2: For Union goods moving within the EU, via a third country, proving their Union status.
What is TIR transit?
An international customs transit system for road transport that simplifies and accelerates the transport of goods between countries through the use of sealed vehicles. It enables the transport of goods without the repeated and time-consuming payment of duties and taxes at intermediate borders, as the duties are covered by an international guarantee.
What is T2L?
Document proving that the goods have a Community character, i.e. they are in free circulation within the European Community.
What is EUR 1?
European certificate of origin required for exports to third countries (e.g. EFTA, Turkey), to allow exemption or reduction of customs duties upon import.
What is ATR?
A customs document used in trade between the European Union (EU) and Turkey. It allows exemption from customs duties for goods imported/exported between the two parties.
What is Carne ATA?
International customs document that allows the temporary import/export of goods without payment of duties and taxes, for up to and one year. It is mainly used for professional equipment, trade samples and exhibition goods.
What is Regime 42?
It allows the import of non-EU goods into the EU without direct payment of VAT upon import, provided that the goods are shipped directly to another EU member state. VAT is paid in the country of destination of the goods.
What are special procedures?
Procedures (e.g., inward/outward processing) that allow temporary import or processing with reduced or suspended duties.
Documents & Processes
Which documents do I need for import customs clearance?
- Commercial Invoice.
- Packing List.
- Transport document (B/L, CMR, or Air Waybill depending on mode).
- Certificates of origin (EUR.1, ATR) where required.
- Special permits/certificates for specific goods (e.g., sanitary, ADR).
Not sure which procedure or documents you need?
Contact our customs team — we’ll guide you.